Professional Scrum Master™ Certification Training

Course Package
Exam Voucher by Scrum.org
Official Training Material from Scrum.org
Official PSM E-Book
Highly Experienced & Accredited Instructor
Live Instructor-Led Sessions
Real Life Examples & Case Studies
Exam Voucher by Scrum.org
Official Training Material from Scrum.org
Official PSM E-Book
Highly Experienced & Accredited Instructor
Live Instructor-Led Sessions
Real Life Examples & Case Studies
Target Audience of PSM Certification
The Professional Scrum Master course is for anyone involved in product delivery using the Scrum framework. It is particularly beneficial for those people within an organization accountable for getting the most out of Scrum, including Scrum Masters, managers, and Scrum Team members.
No pre-existing knowledge of Scrum is required to attend.
Pre-requisites of PSM Certification Training
This course is appropriate for students in any industry where teams are working to solve complex problems. The Professional Scrum Master course is for:
-
Practitioners that are interested in starting a career as a Scrum Master
-
Scrum Masters, Agile/Scrum Coaches and consultant looking to improve their use of Scrum
-
Anyone involved in product delivery using Scrum
Professional Scrum Master™ Certification Exam and Certification Information
-
Passing score: 85%
-
Time limit: 60 minutes
-
Number of Questions: 80
-
Format: Multiple Choice, Multiple Answer, True/False
Professional Scrum Master™ (PSM) Certification Journey
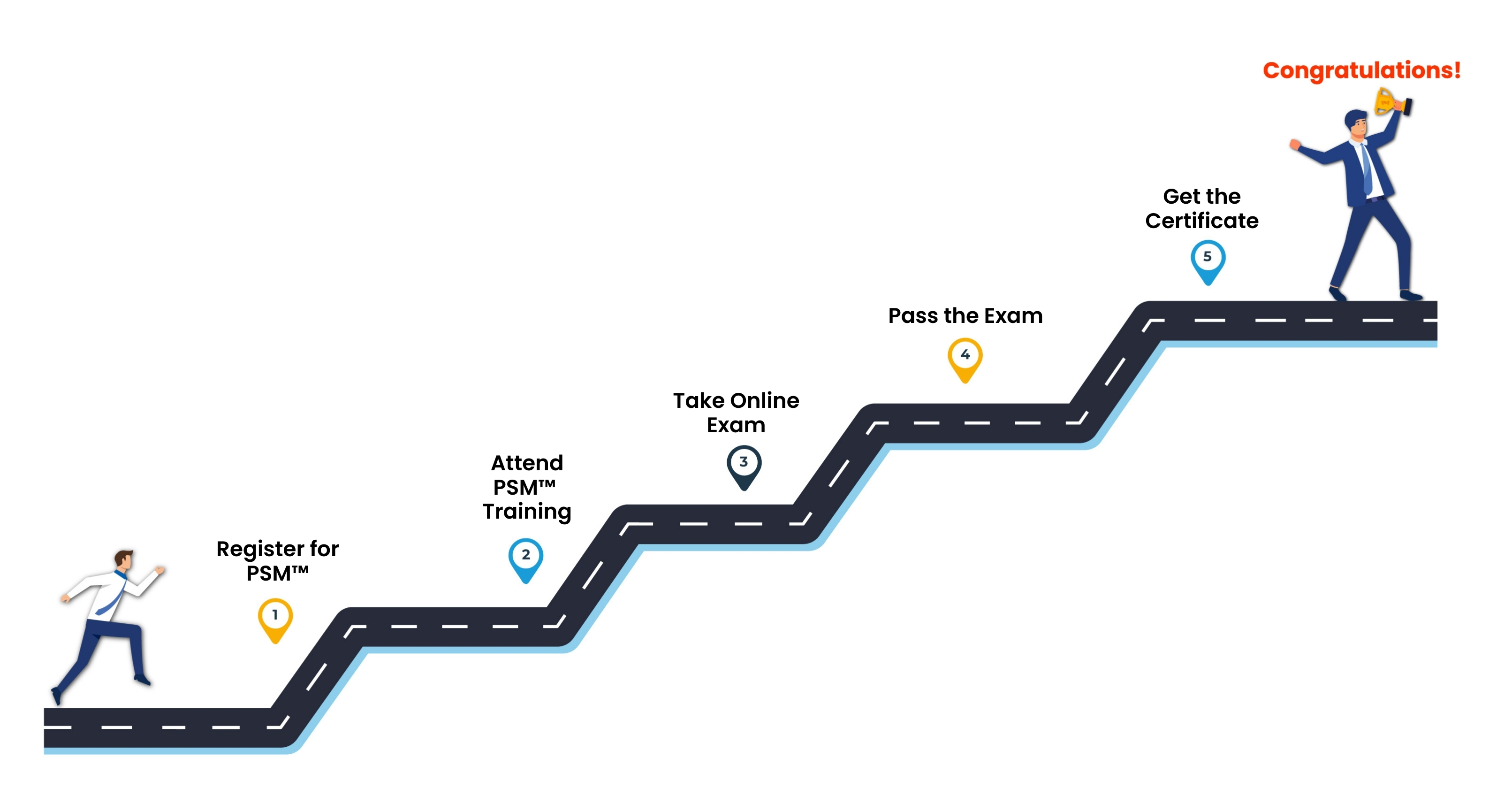
Course Outline
Scrum theory includes time-boxing, and specific roles, rules, and artifacts. All elements of Scrum complement each other to form a consistent whole. All work is performed in Sprints. All base rules, events, and roles are described in the Scrum Guide, the acknowledged Scrum body of knowledge. Each part of Scrum ties back to the principles and theory.
- Scrum Events – Every event in Scrum is an inspect and adapt opportunity. How are these events important? What are the impacts of missing one of these?
- Scrum Role – Every role in Scrum has specific accountabilities. What are their accountabilities? Why are they important? How are they different to traditional project management roles?
- Scrum artefacts – Every artifact in Scrum is transparent so organisation can inspect and adapt based on it. Why are these artefacts important?
- Sprint – The Sprint is the heartbeat of the Scrum framework. What is a Sprint? What are the criteria of a successful Sprint?
Scrum is founded on empirical process theory to deal with the complexity typical to software development. All principles and values of Scrum are based on the fundamental view of software development as creative and complex work.
- How is empirical approach different to defined approach?
- What makes Scrum different to traditional project management approach?
- What is Agile?
- How does Agile relate to Scrum?
- Why should we be Agile and use Scrum?
- In what case is Scrum not suitable?
Check Our Upcoming Batches
Achieve Your PSM Certification Today!
Get Your Certificate in Just 7 Days

Frequently Asked Questions.
Payment options for our Professional Scrum Master (PSM) Certification Training typically include credit/debit card payments, bank transfers, and PayPal. We aim to provide convenient and secure payment methods to accommodate diverse preferences and ensure ease of registration. Additionally, for corporate groups or organizations enrolling multiple participants, we may offer invoicing options and customized payment plans to streamline the process. Our goal is to make the payment experience as smooth and accessible as possible, allowing aspiring PSMs to focus on their training and preparation for certification without any unnecessary hurdles.
Our online virtual classrooms are the primary me answer of doing our Professional Scrum Master (PSM) Certification Training. This model eliminates the need for travel costs and time away from work by allowing participants from different locations to attend the training conveniently from their own devices. Experienced Agile trainers facilitate the virtual training sessions, making use of interactive technologies and collaboration platforms to guarantee a productive and captivating learning environment. Although there may occasionally be live training sessions available in certain places, the default method is virtual, which offers participants flexibility and accessibility from anywhere in the world. Upon enrollment, specific information regarding the training format will be sent.










.png)

